Execute in a Docker Container

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Published: 4/4/2024
The short answer
In Docker, to execute a command inside a container running in detached mode (i.e., the background), you can use the docker exec command as follows:
$ docker exec <container> <command>
Where:
- container is the name or the identifier of a container.
- command is the command you want to run inside of the container.
For example, the following command will execute the ls command inside of the container identified by the name http-server and write the output of the command to the standard output of the terminal:
$ docker exec http-server ls
Easily retrieve this command using Warp’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
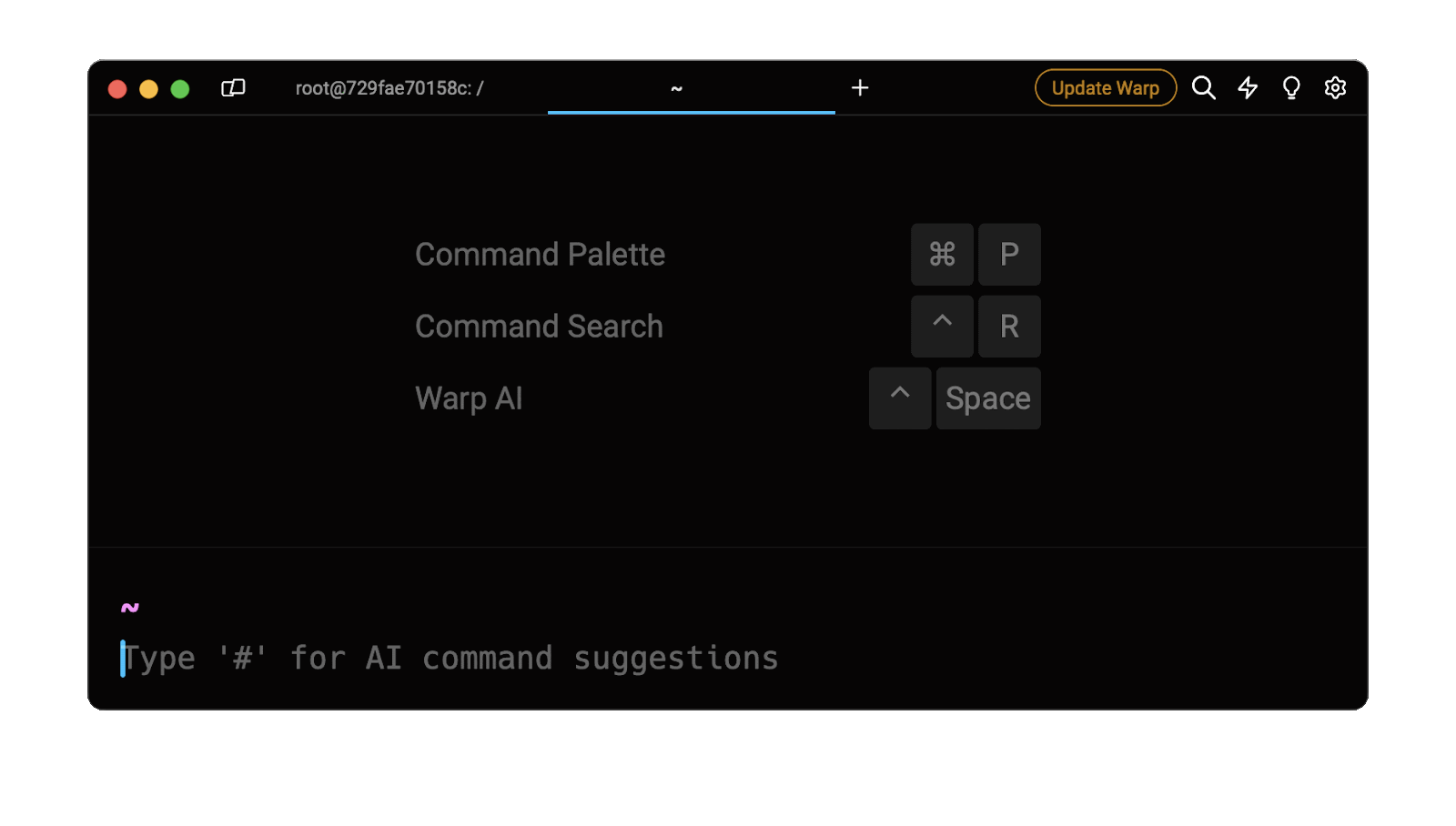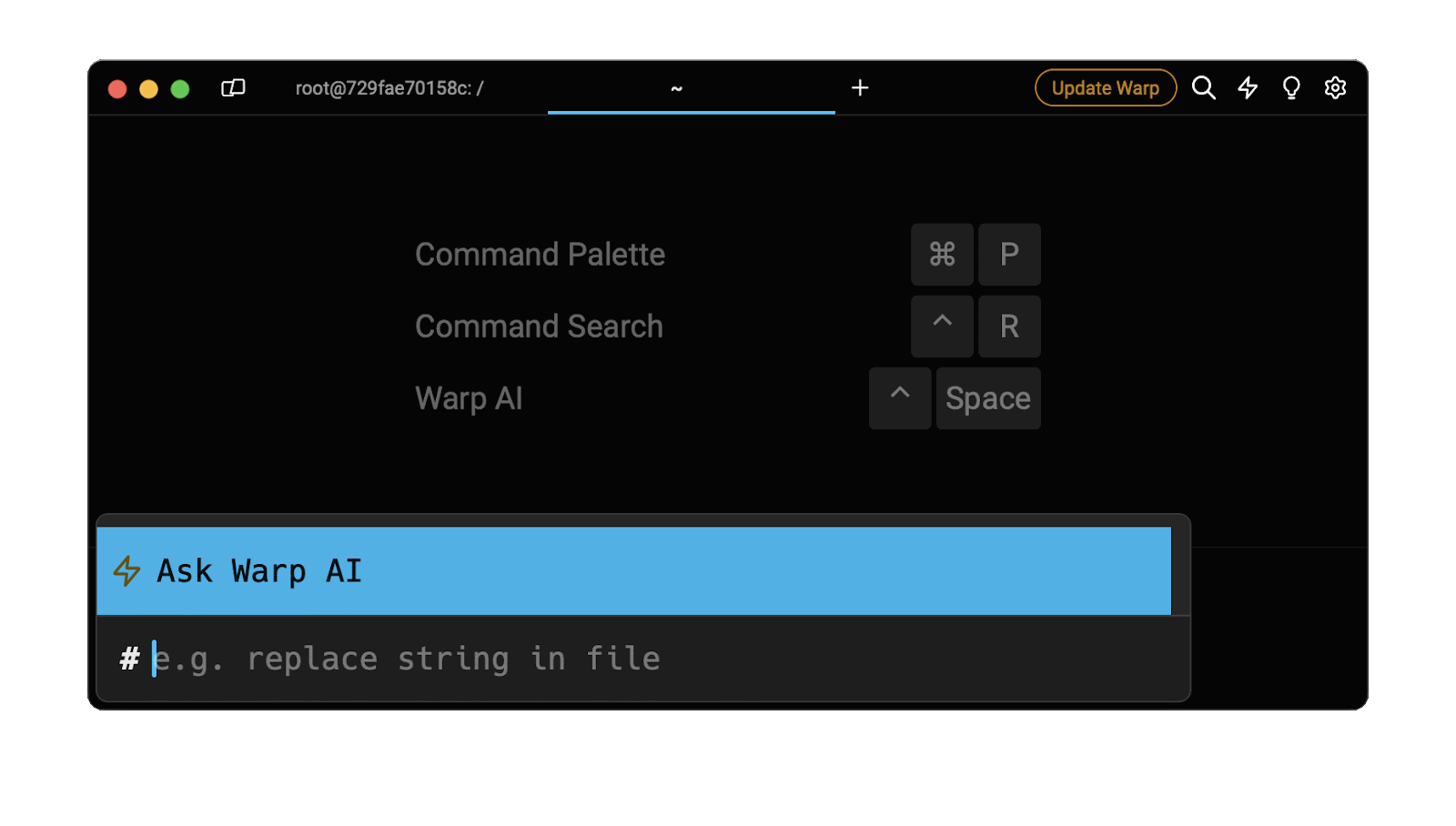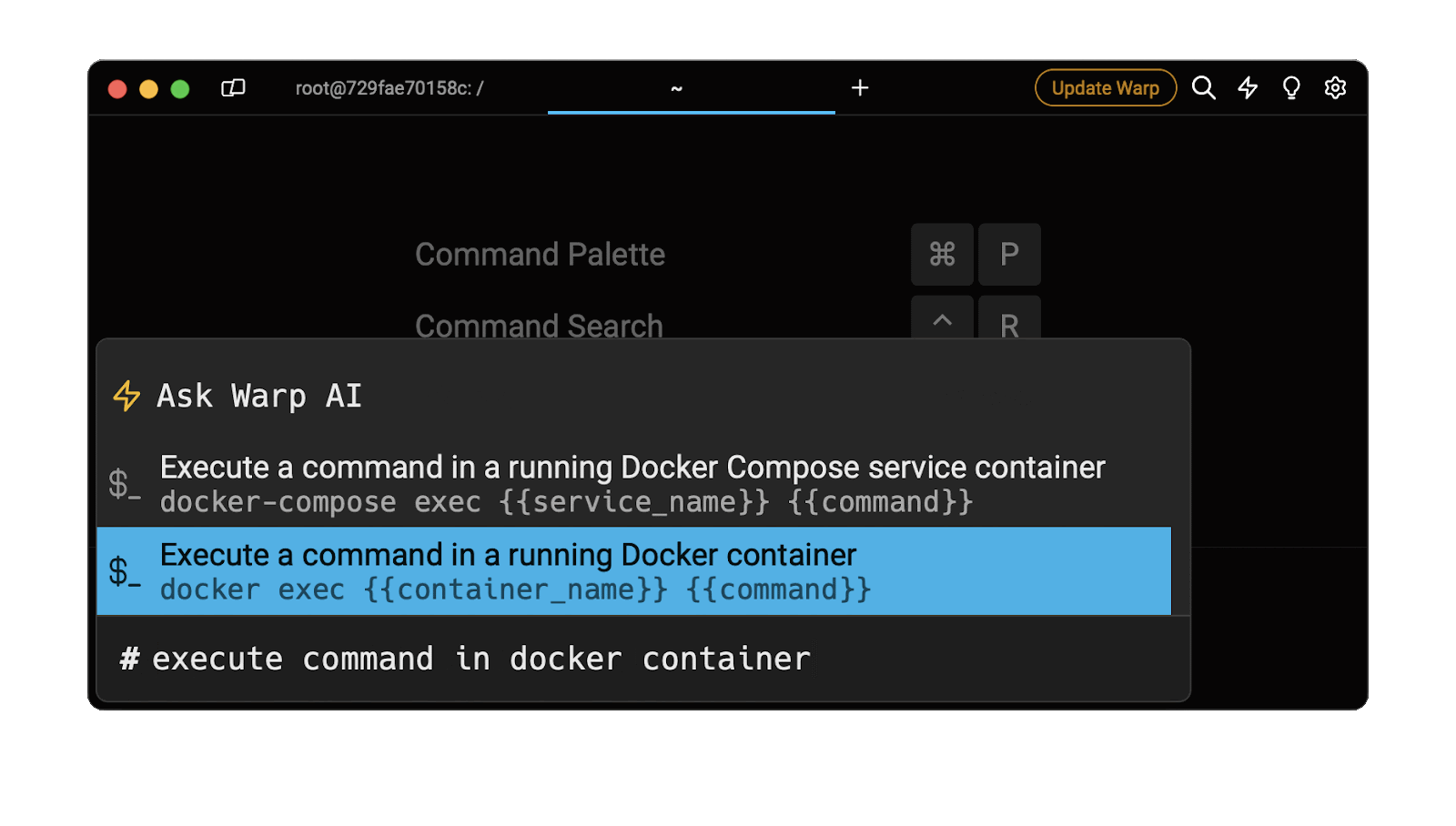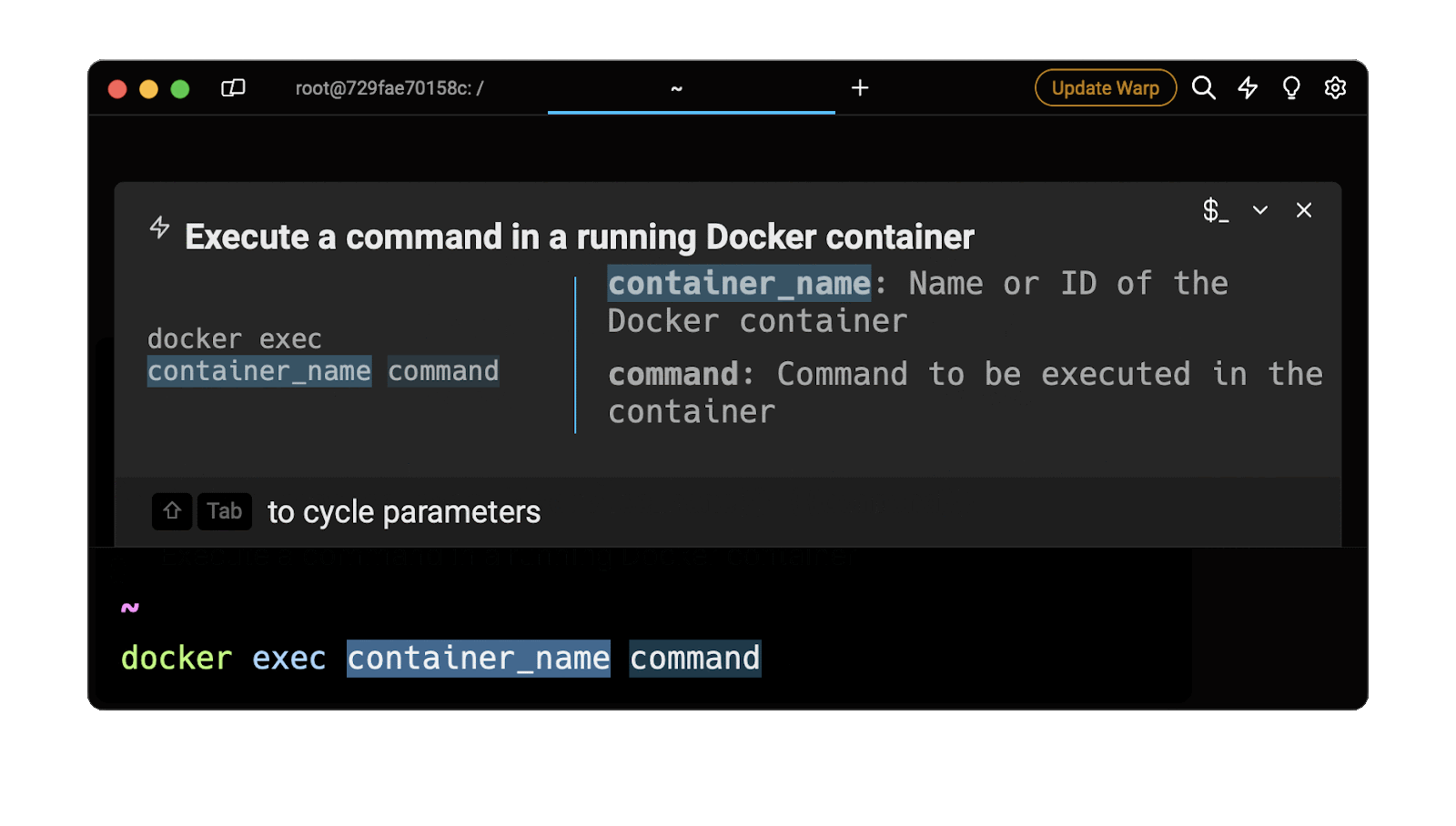
Entering the execute command in docker container in the AI Command Suggestions will prompt a docker command that can be quickly inserted into your shell by pressing CMD+ENTER.
Executing commands as a non-root user
By default, the specified command will be executed inside of the container as the root user.
To execute a command as a non-root user, you can use the docker exec command with the -u flag (short for --user) as follows:
$ docker exec -u >username< -it >container< >command<
Where:
- username is the username or UID of the user the command will be executed as in the form of <name|uid>[:<group|gid>].
For example, the following command will execute the ls command inside of the container named ubuntu as the johndoe user:
$ docker exec -u johndoe ubuntu ls
Executing commands in a specific directory
By default, the specified command will be executed inside of the container in the home directory of the user specified through the -u flag, or by default, in the root directory (i.e., /).
To change the working directory the command will be executed in, you can use the -w flag (short for --workdir) as follows:
$ docker exec -w <path> <container> <command>
Where:
- path is the absolute path of the working directory.
For example, the following command will output the content of the 20240321.log file located in the /app/data/logs/ directory using the cat command in the container identified by the ID 729fae70158c:
$ docker exec -w /app/data/logs 729fae70158c cat 20240321.log
Starting an interactive shell session
To facilitate the execution of commands in a container for debugging, performing administrative tasks, or simply testing, you can start an interactive shell session that provides direct access to the container's shell using the -it flags (short for --interactive and --tty) as follows:
$ docker exec -it <container> <shell>
Where:
-
-it is used to interactively execute commands inside a container.
-
shell is the absolute path to a shell binary installed in the container.
For example, the following command will start an interactive shell session using Bash in the container named ubuntu:
$ docker exec -it ubuntu /bin/bash
You can learn more about containers and Bash by reading our other article on how to run a Bash shell in Docker.
Using shell expansions
By default, any shell expansions specified in the command executed by the docker exec command will be expanded by the shell the command is executed from on the local machine.
For example, when running the following command, the ~ expression will be expanded into the path of the user's home directory on the local machine:
$ docker exec 729fae70158c ls ~
To get around this problem, you can pass your command as sub-command of the /bin/bash -c command as follows:
$ docker exec <container> /bin/bash -c '<command>'
For example, when running the following command, the ~ expression will be expanded into the path of the johndoe user's home directory (i.e., /home/johndoe) in the container:
$ docker exec -u johndoe 729fae70158c /bin/bash -c 'ls ~'
Executing a command with temporary environment variables
By default, the commands executed through the docker exec command inherit the environment variables set at the time the container is created.
To override existing environment variables or set additional ones, you can use the -e flag (short for --env) as follows:
$ docker exec -e <variable>=<value> [-e <variable>=<value> …] <container> <command>
Where:
- variable is the name of the environment variable.
- value is the value assigned to that variable.
For example, the following command will set the NODE_ENV environment variable as development and execute the node index.js command in the /app directory of the container named web-server:
$ docker exec -w /app -e NODE_ENV=development web-server node index.js
Using an environment file
Alternatively, you can use the --env-file flag to pass a file containing a list of environment variables as follows:
$ docker exec --env-file <path> <container> <command>
Where:
- path is the relative or absolute path to the environment file.
For example, the following command will use the variables specified in the .env.dev file located in the current working directory and execute the npm run test command in the /app directory of the container named web-server:
$ docker exec -w /app --env-file .env.dev web-server npm run test
If you want to save the changes made to a container using the docker exec command, you can read our other article on how to save a Docker container as an image.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
Override the Container Entrypoint With docker run
Learn how to override and customize the entrypoint of a Docker container using the docker run command.
The Dockerfile ARG Instruction
Learn how to define and set build-time variables for Docker images using the ARG instruction and the --build-arg flag.

Start a Docker Container
Learn how to start a new Docker container from an image in both the foreground and the background using the docker-run command.

Stop All Docker Containers
How to gracefully shutdown running containers and forcefully kill unresponsive containers with signals in Docker using the docker-stop and docker-kill commands.

Use An .env File In Docker
Learn how to write and use .env files in Docker to populate the environment of containers on startup.
Run SSH In Docker
Learn how to launch and connect to a containerized SSH server in Docker using password-based authentication and SSH keys.

Launch MySQL Using Docker Compose
Learn how to launch a MySQL container in Docker Compose.
Expose Docker Container Ports
Learn how to publish and expose Docker container ports using the docker run command and Dockerfiles.
Restart Containers In Docker Compose
Learn how to restart and rebuild one or more containers in Docker Compose.

Output Logs in Docker Compose
Learn how to output, monitor, customize and filter the logs of the containers related to one or more services in Docker Compose

Rename A Docker Image
Learn how to rename Docker images locally and remotely using the docker tag command.
Understand healthcheck in Docker Compose
Learn how to check if a service is healthy in Docker Compose using the healthcheck property.

