The short answer
In Docker, a container hostname is a label assigned to a container to uniquely identify it within a network to facilitate the communication between containers.
To set the hostname of a Docker container during its creation, you can use the docker run command with the --hostname flag as follows:
Where:
- docker run is used to create and run Docker containers.
- hostname is the hostname of the container.
- image is the Docker image the container will be created from.
For example:
This command launches a new container based on the latest version of the ubuntu image and sets its hostname to my-docker-app.
Note that the container's hostname will default to its ID if not specified upon creation.
Easily retrieve this command using Warp’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
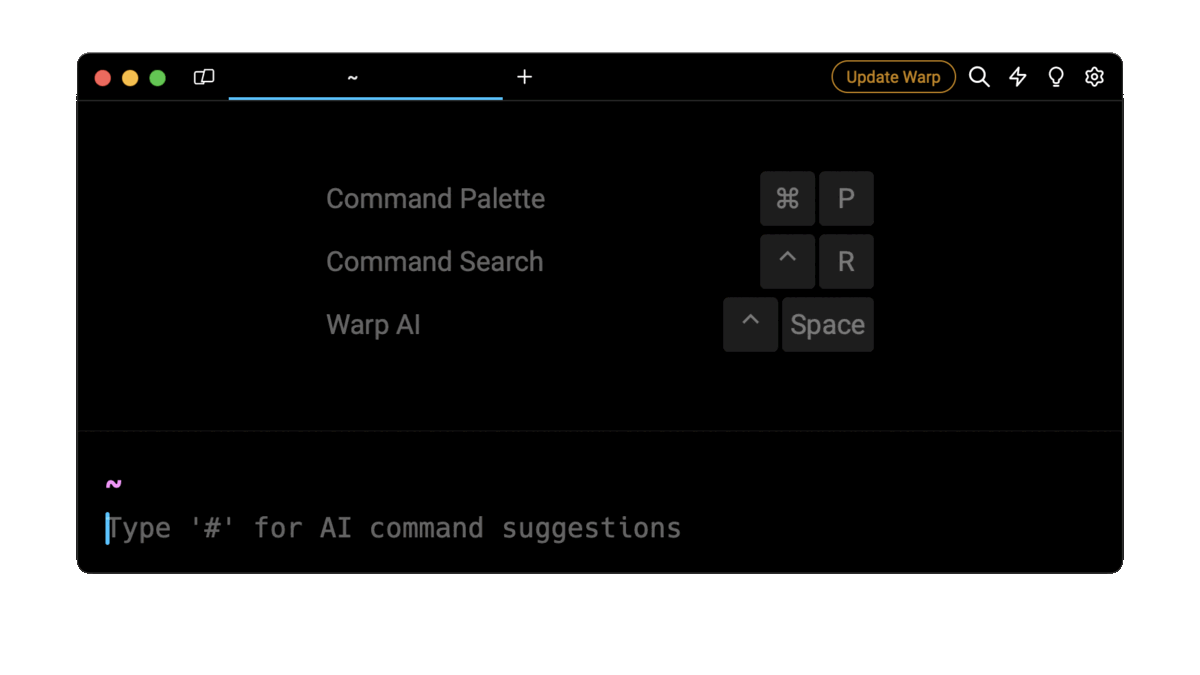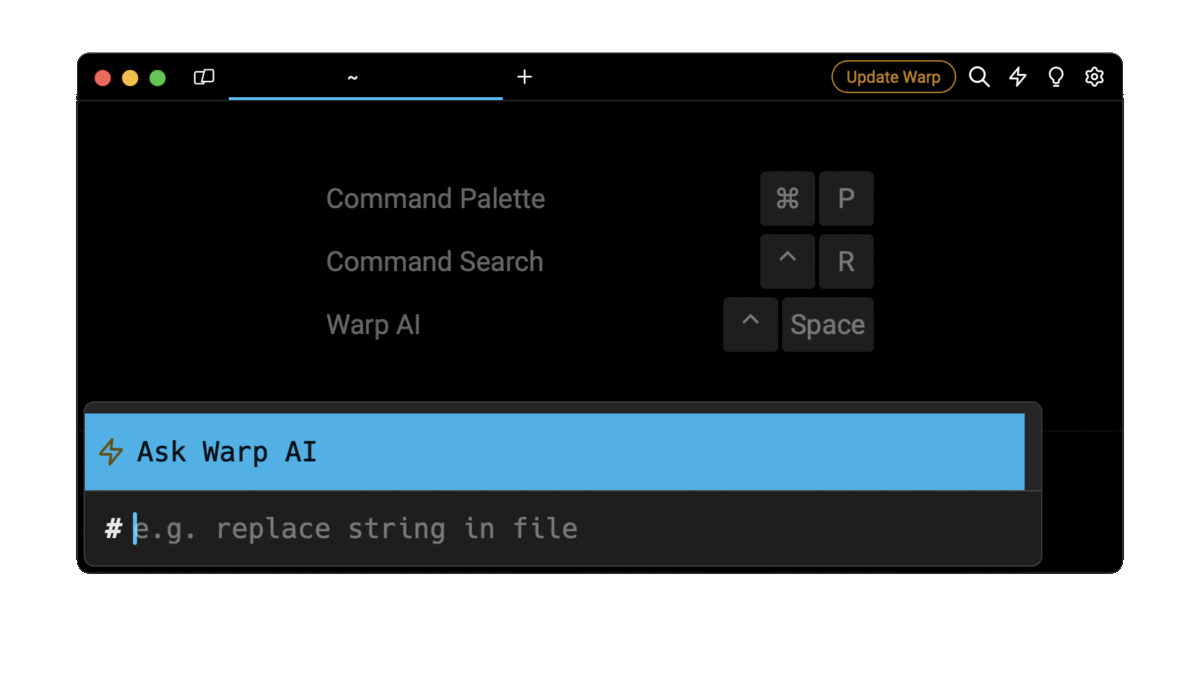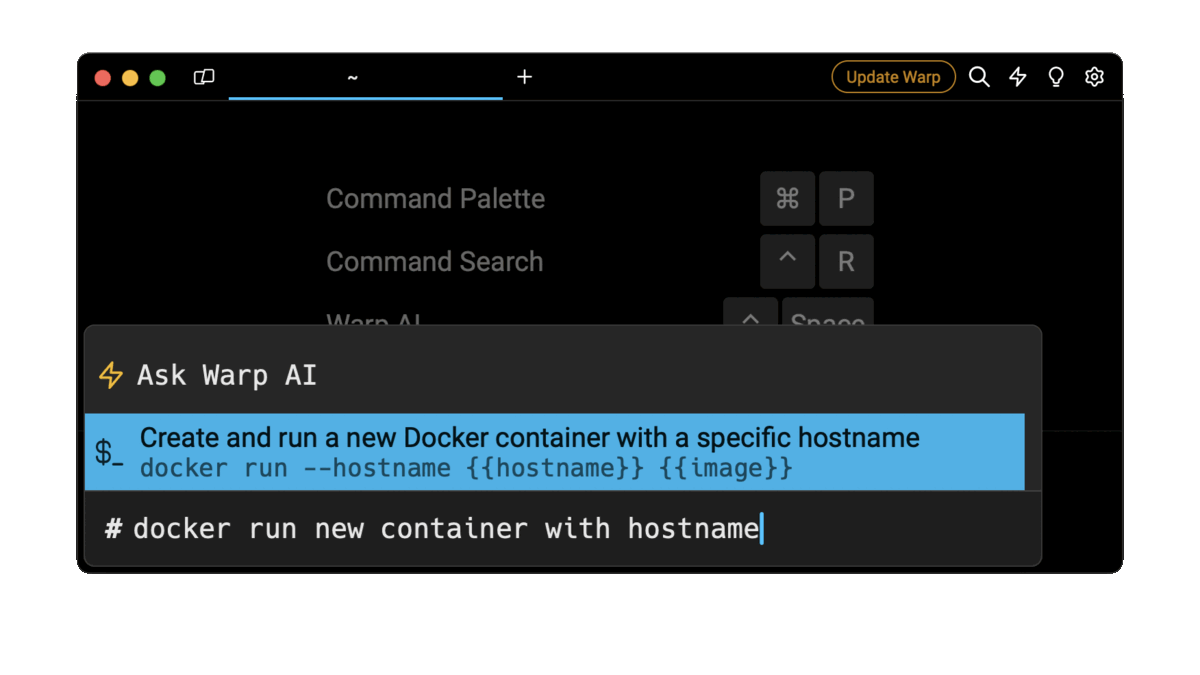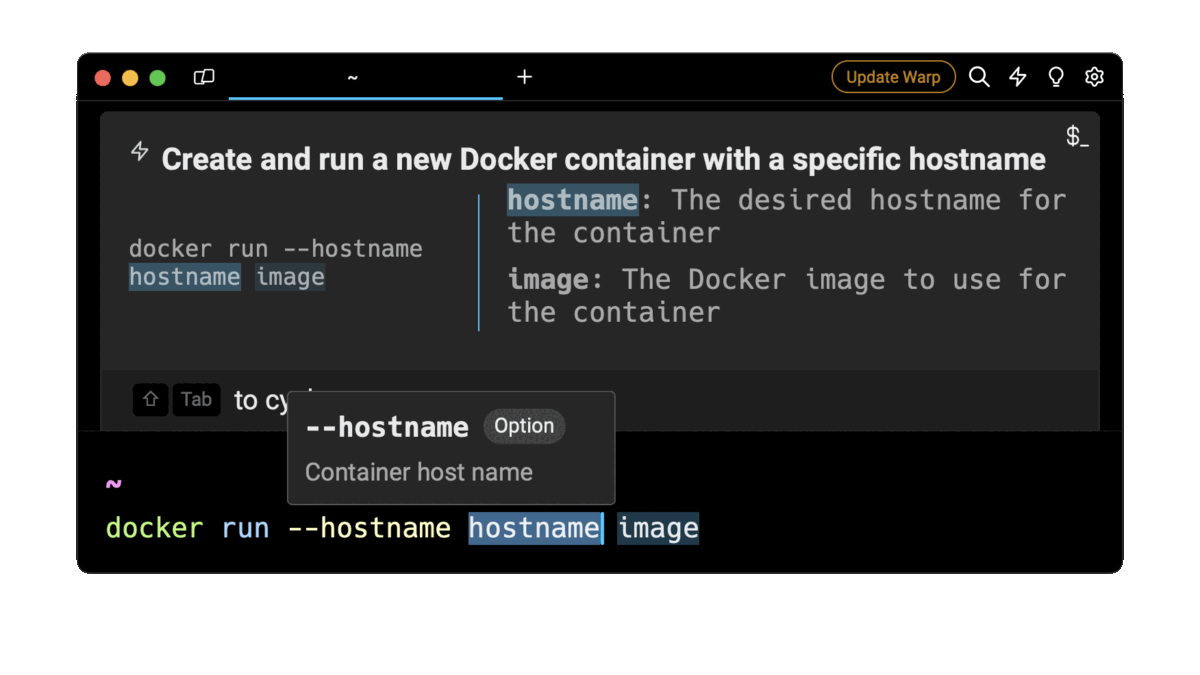
Entering docker run new container with hostname in the AI Command Suggestion will prompt a docker command that can then quickly be inserted into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER.
Differences between a container hostname and name
In Docker, container hostnames are used for internal network communication between applications running in different containers. They are, by default, visible to the other containers using the same network unless configured for external access. Container hostnames can be dynamically assigned but must be unique within a specific network.
On the other hand, container names serve as identifiers for users. They need to be unique among all running containers on the Docker host, serving as distinct labels for container management.
Matching the container hostname with the name of the host
To match the hostname of a Docker container with the one of the host machine, you can use the docker run command in following way:
Where:
- The hostname command is used to output the name of the current host.
- The $() command substitution syntax is used to execute the specified command and replace it at runtime with its output.
Note that this command substitution mechanism ensures that the container's hostname is synchronized with the hostname of the host system.
For example:
This command launches a new container based on the latest version of the ubuntu image and dynamically sets its hostname to the current name of the host machine.
Getting a container's hostname using the command-line
To get the hostname of a Docker container, you can use the docker inspect command with the --format flag as follows:
Where:
- Docker inspect provides information about Docker containers.
- --format specifies the template to use to format the command's output.
- '{{.Config.Hostname}}' is a format template used to extract the container's hostname.
For example, you can use the docker ps -a command to output the list of running and stopped containers:
Then use the docker inspect command to get the hostname of a specific container:
You can learn how the hostname within Docker containers, including Postgres containers, influences networking and communication setups from this article.
Getting a container's hostname using a Python script
To get the hostname of a specific Docker container in Python, you can first install the docker package with pip:
Then access the Docker API using the docker module:
Written by

Utsav Poudel
Filed Under
Related Articles
Override the Container Entrypoint With docker run
Learn how to override and customize the entrypoint of a Docker container using the docker run command.
The Dockerfile ARG Instruction
Learn how to define and set build-time variables for Docker images using the ARG instruction and the --build-arg flag.

Start a Docker Container
Learn how to start a new Docker container from an image in both the foreground and the background using the docker-run command.

Stop All Docker Containers
How to gracefully shutdown running containers and forcefully kill unresponsive containers with signals in Docker using the docker-stop and docker-kill commands.

Use An .env File In Docker
Learn how to write and use .env files in Docker to populate the environment of containers on startup.
Run SSH In Docker
Learn how to launch and connect to a containerized SSH server in Docker using password-based authentication and SSH keys.

Launch MySQL Using Docker Compose
Learn how to launch a MySQL container in Docker Compose.
Execute in a Docker Container
Learn how to execute one or multiple commands in a Docker container using the docker exec command.

Expose Docker Container Ports
Learn how to publish and expose Docker container ports using the docker run command and Dockerfiles.
Restart Containers In Docker Compose
Learn how to restart and rebuild one or more containers in Docker Compose.

Output Logs in Docker Compose
Learn how to output, monitor, customize and filter the logs of the containers related to one or more services in Docker Compose

Rename A Docker Image
Learn how to rename Docker images locally and remotely using the docker tag command.